Poor understanding of LED strip voltage can lead to dim lighting or damaged products. Knowing internal circuitry and voltage requirements ensures reliable performance.
LED strip lights are constructed from LEDs, resistors, PCBs, and other components. Proper voltage selection prevents voltage drops, ensures consistent brightness, and protects against premature failure, benefiting project outcomes.
Exploring the internal schematic of LED strip lights can improve your installation outcomes dramatically. Read further to master voltage requirements and internal structures.
What Are the Key Components of LED Strip Lights?
Incorrect knowledge of components can cause poor lighting outcomes and even product damage, frustrating your clients and causing installation issues.
LED strip components include LED beads, resistors, capacitors, diodes, PCBs, and copper traces. Each plays a critical role in emitting consistent and reliable lighting.
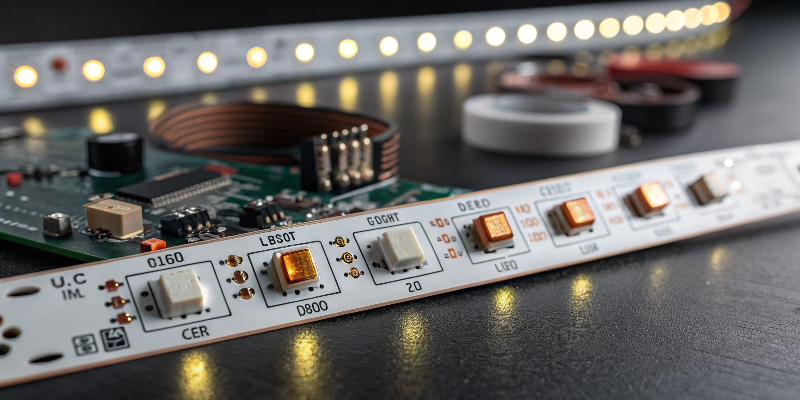
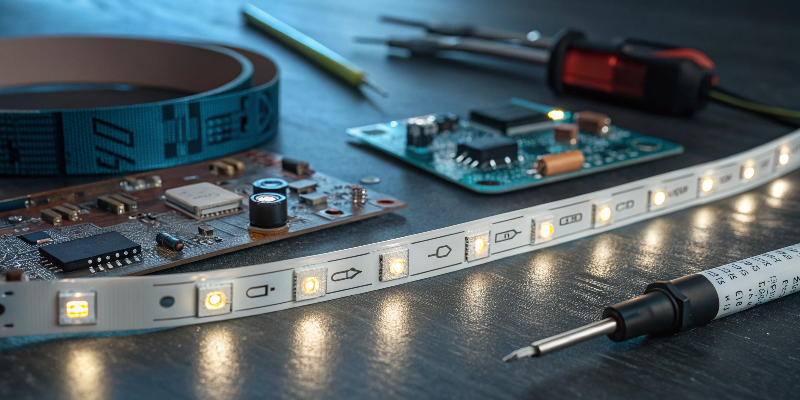
LED strip lights consist of various components working together for optimal performance. LED beads1 emit the actual light, varying in brightness based on size, type, and arrangement. The printed circuit board (PCB)2 holds all components, offering flexibility and easy installation. Resistors control current flow, preventing LEDs from damage caused by excessive currents. Capacitors stabilize power, reducing flickering issues common in advanced LED strips. Diodes ensure current flows in one direction, protecting LED beads from reverse currents and enabling color control in RGB setups. Finally, copper traces on the PCB distribute electrical current evenly across the LED strip, ensuring consistent brightness.
Component Functions Overview:
| Component | Function | Impact on Performance |
|---|---|---|
| LED Beads | Emit visible light | Brightness, color accuracy |
| PCB | Mounts components, flexibility | Installation ease, durability |
| Resistors | Control current flow | LED protection, lifespan |
| Capacitors | Stabilize voltage, reduce flicker | Lighting consistency |
| Diodes | Ensure current direction, RGB control | Color control, component protection |
| Copper Traces | Electrical current distribution | Even brightness, voltage stability |
Clearly understanding each component’s role helps you select high-quality LED strips that meet your project’s unique requirements, ensuring client satisfaction and minimizing post-installation issues.
How Does LED Forward Voltage Influence LED Strip Performance?
Misunderstanding LED forward voltage can result in dimming or LED damage, negatively impacting client perception and increasing maintenance costs.
Forward voltage (VF) is the minimum voltage needed for LEDs to emit light. Different LED colors require different forward voltages, influencing brightness and compatibility with power supplies.
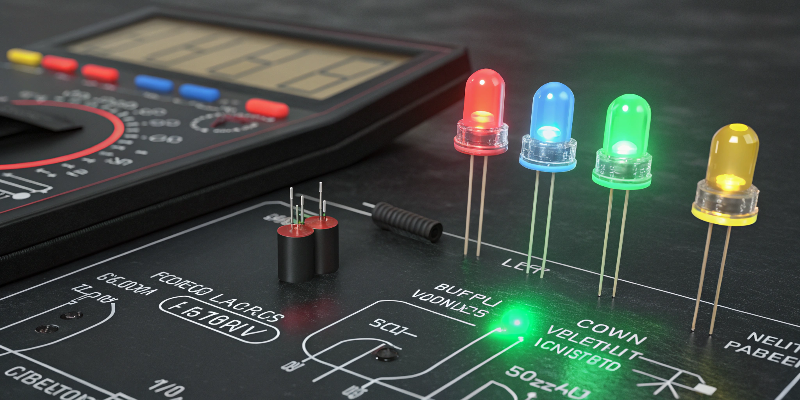

The forward voltage of an LED is critical for proper functioning. LEDs have specific voltage requirements varying by color, directly influencing brightness and lifespan. Incorrect forward voltage supply leads to reduced brightness or premature LED failure. Understanding this allows accurate matching of LED strips to power sources.
Forward Voltage by LED Color:
| LED Color | Forward Voltage (VF) |
|---|---|
| Red | 1.8–2.1 V |
| Amber | 2.0–2.2 V |
| Yellow | 1.9–2.2 V |
| Green | 2.0–3.1 V |
| Blue | 3.0–3.7 V |
| White | 3.0–3.4 V |
When Tom, a client from the US, overlooked LED forward voltage in his projects, he faced dimming and customer complaints. After properly matching forward voltage to power supply requirements, these issues vanished. Thus, understanding LED forward voltage ensures optimal lighting quality and reliability.
Series vs. Parallel: Which LED Strip Configuration is Better?
Incorrect configuration choices cause uneven brightness or lighting failures, frustrating your clients and complicating installations.
Series configurations add voltage requirements while maintaining constant current. Parallel configurations maintain voltage but distribute current, affecting brightness uniformity and overall complexity.
Comparing Series and Parallel Configurations:
| Feature | Series LED Strips3 | Parallel LED Strips4 |
|---|---|---|
| Voltage Behavior5 | Voltages add up | Voltage constant |
| Current Flow | Same current throughout | Current divided among LEDs |
| Installation Ease | Simple | Complex |
| Failure Impact | Single LED failure affects entire circuit | Single LED failure doesn’t affect entire circuit |
| Brightness | Even brightness (initially) | Brightness varies if poorly balanced |
Series configurations are simpler, needing fewer connections, ideal for smaller installations. However, one LED failure stops the entire circuit. Parallel configurations allow continued operation despite failures and enable advanced lighting effects but require careful current balancing. Understanding these helps you choose the correct setup for your project’s demands.
Why Does Voltage Drop Occur in LED Strips?
Voltage drop creates uneven brightness, causing dissatisfied clients and leading to costly troubleshooting.
Voltage drop occurs due to resistance in long LED strips. It causes brightness dimming at strip ends, negatively affecting lighting uniformity.

Voltage drop significantly impacts lighting projects. It occurs naturally due to resistance as current travels along lengthy strips or thin copper traces. Symptoms include gradually dimmer lighting from the power source toward the strip’s end, frustrating users expecting uniform illumination.
Tom previously encountered serious voltage drop issues in large commercial projects, leading to client complaints and expensive repairs. By adopting thicker PCBs, parallel wiring, and higher voltage strips, he solved these problems, greatly improving client satisfaction.
Causes of Voltage Drop:
- Long LED strips
- Thin copper traces or wires
- High electrical resistance
- Incorrect voltage selection
Careful planning and correct product selection prevent these issues, ensuring consistent brightness across installations.
How to Effectively Reduce Voltage Drop in LED Strips?
Voltage drop causes client dissatisfaction and frequent maintenance, negatively impacting your project’s efficiency and profitability.
Reducing voltage drop involves higher voltage LED strips, shorter lengths, parallel wiring, and thicker PCB materials. These solutions maintain consistent brightness and reliable LED performance.
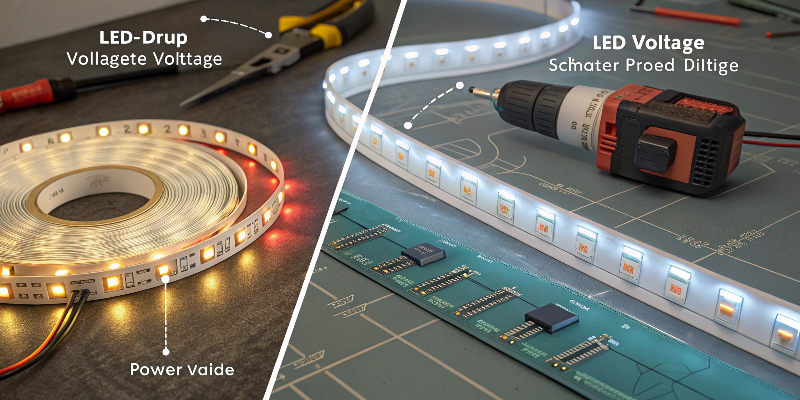
Effective strategies to reduce voltage drop include selecting higher-voltage LED strips (24V, 48V), shortening strip lengths, parallel wiring connections, and using thicker copper in PCBs. Each method has unique advantages and disadvantages, shown in this comparison:
Methods to Reduce Voltage Drop:
| Method | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Higher Voltage | Reduces voltage drop efficiently | Requires safety precautions |
| Shorter Strip Length | Simplest method | Limits lighting applications |
| Parallel Wiring | Uniform brightness across multiple strips | Installation complexity increases |
| Thicker PCB | Durable, reduces resistance effectively | Slightly higher initial cost |
Tom utilized parallel wiring and thicker PCBs in his installations, significantly reducing voltage drop issues. Though initially increasing costs slightly, these methods drastically enhanced lighting quality and customer satisfaction, reducing maintenance expenses long-term.
Must LED Strips Receive Exact Specified Voltage?
Supplying incorrect voltage can ruin LED strips or reduce their brightness significantly, frustrating your customers and damaging your professional credibility.
LED strips tolerate slight voltage deviations. However, exact voltage is recommended to avoid performance issues and extend product lifespan.
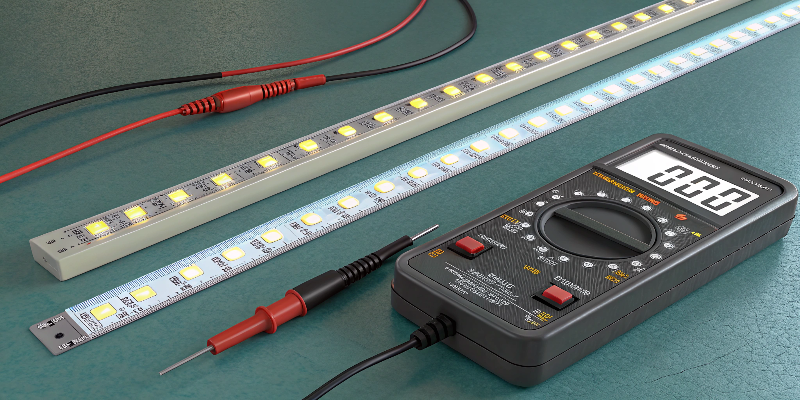

LED strips operate best when receiving precise specified voltage. LEDs have small voltage tolerance margins. Slightly lower voltages reduce brightness without harming LEDs. Slightly higher voltages initially enhance brightness but risk overheating, causing rapid LED degradation6. Ensuring precise voltage matching7 avoids these risks, delivering consistent lighting performance and enhancing client satisfaction.
Voltage Tolerance Impact:
- Slightly Lower Voltage: Reduced brightness, safe operation.
- Exact Voltage: Optimal brightness, maximum lifespan.
- Slightly Higher Voltage: Temporary brightness increase, risk of overheating and damage.
Tom discovered precise voltage matching2 improved overall customer satisfaction. Small initial investments in accurate power supplies significantly lowered maintenance costs and boosted client retention.
Conclusion
Understanding LED strip internal components, voltage requirements, and voltage drop prevention ensures optimal brightness, reliability, and satisfied clients in every lighting installation.
-
Explore this link to understand how LED beads influence brightness and color accuracy, crucial for your lighting projects. ↩
-
Learn about the importance of PCBs in LED strips for installation ease and durability, enhancing your project outcomes. ↩ ↩
-
Explore the benefits of Series LED Strips to understand their simplicity and ideal use cases for smaller installations. ↩
-
Discover the advantages of Parallel LED Strips, including their resilience to failures and ability to create advanced lighting effects. ↩
-
Learn about voltage behavior in LED configurations to make informed decisions for your lighting projects. ↩
-
Learning about LED degradation will help you avoid common pitfalls and maintain the quality of your lighting solutions. ↩
-
Understanding precise voltage matching can help you ensure optimal performance and longevity of your LED strips, enhancing customer satisfaction. ↩







